LED headlights have become increasingly popular in recent years due to their numerous advantages over traditional halogen or HID headlights. One of the unique features of LED headlights is the presence of fans. In this article, we will explore the reason why LED headlights have fans and how they contribute to the overall performance and longevity of the headlights.
LEDs generate heat
LEDs are semiconductor devices that convert electrical energy into light. However, this conversion process is not 100% efficient, and a significant amount of energy is converted into heat. As the LEDs operate, they generate heat which, if not properly dissipated, can cause a rise in temperature. This temperature increase can negatively impact the performance and lifespan of the LEDs.
Thermal management is crucial
To maintain optimal performance and extend the lifespan of LED headlights, thermal management becomes crucial. Proper thermal management ensures that the LEDs operate within their recommended temperature range, preventing premature failure and performance degradation.
Riders will find a problem. LED headlight bulbs will become darker and darker after being used for a long time. Here we learn a new term, LED light failure.
What is LED light failure?
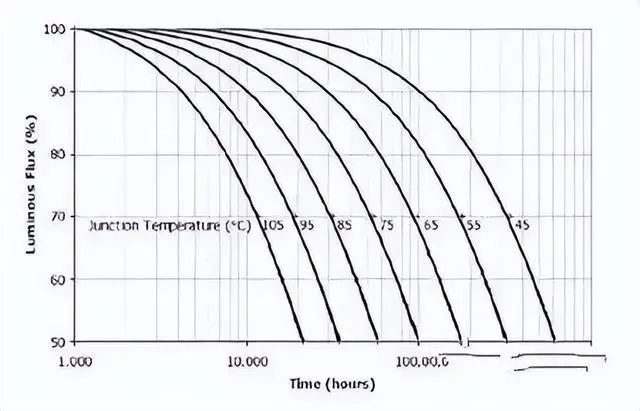
LED light attenuation means that after the LED is lit for a period of time, its light intensity will decrease compared to the initial light intensity and cannot be restored. That is, the reduced part is called the light attenuation of the LED. At present, my country has not yet formulated a definition and general standard for LED light failure. GB/T24823-2009 requires that the luminous flux maintenance rate stipulated in the LED module performance requirements is at the ignition point of 3000 hours. The luminous flux maintenance rate should not be less than 92%. Only a certain product of indoor lighting fixtures is tested. The industry generally calls on the country to formulate LED lighting standards as soon as possible. Declining standards.
What is the reason for LED light failure?
LED light decay is the phenomenon of irreversible damage to light source components that exceeds the temperature resistance limit.
As we all know, after the LED is working, its light intensity will decrease as the chip junction temperature increases, and the light efficiency will decrease accordingly. This is an inherent physical characteristic of semiconductors that changes with temperature. As long as a component of the light source does not exceed the temperature limit and be damaged, the LED will stop After the temperature drops to the original value, the light intensity will return to the original value. That is to say, no matter how long the LED is operated or repeated many times, as long as the initial light intensity remains unchanged, it cannot be considered as light failure. Light failure means that the light source exceeds the limit due to long-term working temperature. If the light intensity cannot return to the initial value, it is called light decay. That is, the irreversible decrease in luminous flux is the real meaning of light decay. LED light decay is the phenomenon of irreversible damage to light source components that exceeds the temperature resistance limit.
LED lights become dimmer as they are used because LED lights suffer from light attenuation.
The light attenuation of LED lamp products is the weakening of the light signal during transmission. At this stage, the LED products produced by global LED manufacturers have different levels of light attenuation. High-power LEDs also have light attenuation, which is directly related to temperature. Mainly It is determined by the chip, phosphor and packaging technology. At present, the light failure of white LEDs on the market is one of the primary problems in entering civil lighting.
Light decay generally refers to its luminous flux. When charging the surface of the photosensitive drum, as the charge accumulates on the surface of the photosensitive drum, the potential continues to increase, and finally reaches the "saturation" potential, which is the highest potential. The surface potential will decrease with the passage of time. Generally, the potential during operation is lower than this potential. The process of this potential naturally decreasing with time is called the "dark decay" process.
When the photosensitive drum is scanned and exposed, the potential in the dark area (referring to the surface of the photoconductor that is not exposed to light) is still in the dark decay process; in the bright area (referring to the surface of the photoconductor that is exposed to light) the carrier density in the photoconductive layer increases rapidly. The conductivity rises rapidly, forming a photoconductive voltage, the charge disappears rapidly, and the surface potential of the photoconductor also drops rapidly. Call it "light decay."
It is a very common phenomenon that LED lights become dimmer with use. In addition to light decay, the reasons that can make LED lights dim are nothing more than the following two points.
01 Drive damaged
LED lamp beads are required to work at low DC voltage. We need to convert the vehicle electricity into the electricity required by the lamp beads, so we need a device called "LED constant current drive power supply".
Theoretically speaking, as long as the parameters of the driver match the lamp bead board, it can continue to supply power and be used normally. The inside of the driver is relatively complex. Failure of any device (such as capacitor, rectifier, etc.) may cause the output voltage to change, which in turn causes the lamp to dim.
Driver damage is the most common fault in LED lamps, and it can usually be solved by replacing the driver.
02 LED burned out
The LED itself is composed of lamp beads one by one. If one or part of them does not light up, it will inevitably make the entire lamp dim. Lamp beads are usually connected in series first and then in parallel - so if a certain lamp bead burns out, a batch of lamp beads may not light up.
There are obvious black spots on the surface of the burnt lamp bead. Find it, connect a wire to the back of it, short-circuit it, or replace it with a new lamp bead, which can solve the problem.
Occasionally an LED burns out, maybe by chance. If it burns out frequently, you need to consider the driver problem - another manifestation of driver failure is burned out lamp beads.
The principle of LED intolerance to temperature
LED lights are typical cold light sources with a lower color temperature. Compared with halogen lights, the infrared light content in LED light is much lower. Therefore, when the LED light source shines on the skin, the somatosensory temperature is much lower than when the halogen lamp (bulb with filament) shines on the skin.
This will give people the feeling that LED lights generate low heat. This is also true. The heat generated by LEDs is much lower than that of halogen lamps at the same power. However, LEDs are semiconductor devices that are temperature sensitive and not resistant to high temperatures. Poor heat dissipation will seriously shorten the life and brightness of LED lamp beads. Halogen lamps are high temperature resistant and do not require heat dissipation at all. This is why LED bulbs either have heat sinks or fans.
Even the 3-5w LED flashlight has a heat sink in order to work stably for a long time. When LED is working, only about 25% of the electricity is converted into light energy, and the rest of the electricity is converted into heat and dissipated. LEDs are particularly sensitive to temperature, and heat energy affects the performance of LEDs. If the heat cannot be dissipated in time, it will first cause light attenuation and a decrease in brightness. When the ambient temperature is 25°C, for every 1°C increase in LED light intensity, the LED light intensity will correspondingly decrease by 1%. As the LED temperature continues to rise, the LED structure will be irreversibly damaged, eventually causing the LED to open circuit and burn out.
In this case, a 30-50w LED car light has about 22-38w of electricity converted into heat. The LED car light is equivalent to a 22w-38w electric heater. Although the power may not seem high, when the heat cannot be dissipated, it will slowly accumulate together, and this temperature cannot be underestimated! Therefore, the heat must be dissipated in time, so the tail of the car's LED headlight bulb is either equipped with a cooling fan or a metal heat sink.
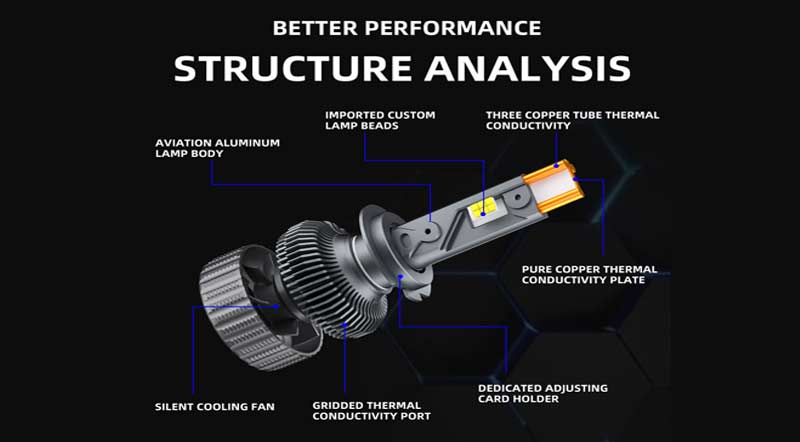
In response to the above problems, if LED headlights want to achieve relatively high power, they must have excellent heat dissipation design. Let’s talk about the factors that affect the heat dissipation design of high-power headlights.
factors that affect the heat dissipation design of high-power headlights.
1.Driver
The driver is an important electronic component for lighting the LED lamp beads. The driver is composed of many electronic components. The higher the luminous efficiency of the LED lamp, the lower the power of the LED device, the smaller the power of the LED lamp beads, and the less heat it emits.
2. LED lamp light efficiency and quality
The size of the lamp bead chip determines the temperature resistance of the LED. Generally speaking, the larger the chip, the higher the temperature resistance of the LED. High-quality chips determine the durability of the LED lamp bead.
3. Fan quality and speed
The high-speed running fan is also an important component for heat dissipation of LED headlights. The quality and speed of the fan determine the heat dissipation efficiency of the LED headlights.
4. Heat pipes and copper plates
High-power LED headlights generally use heat pipes and copper substrates as important materials to conduct heat from the lamp beads. The heat pipes and copper substrates will quickly conduct the heat from the LED headlight lamp beads to the radiator, and the fan accelerates the heat loss from the radiator.
5. Radiator
The radiator is an important structural design of the lamp body. A radiator with fine fins will accelerate heat loss.
Conclusion
In summary, LED headlights have fans to help dissipate heat generated during operation. The fans ensure that the LEDs remain within their optimal temperature range, preventing premature failure and performance degradation. By effectively managing heat through active cooling, LED headlights with fans provide enhanced reliability, performance, and longevity, making them an excellent choice for vehicle owners seeking high-quality lighting solutions.